Function code | Name | Detailed instruction of parameters | Default value | Modify | ||
P02.00 | Motor type 1 | 0: Asynchronous motor 1: Synchronous motor Note: Switch the current motor by the switching channel of P08.31. | 0 | ◎ | ||
P02.01 | Rated power of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.1– 3000.0kW | Set the parameters of the controlled AM. In order to ensure control performance, set the value of P02.01–P02.05 based on the nameplate parameters. Goodrive35 series VFD provides parameter autotuning function. The accurate parameter autotuning requires proper parameter setup. In order to ensure control performance, configure the motor based on the motor which matches with the VFD. If the gap between motor power and the matched motor is too large, the control performance of the VFD will be deteriorated greatly. Note: P02.02–P02.10 can be initialized by resetting rated motor power P02.01. | Depend on model | ◎ | |
P02.02 | Rated freque- ncy of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.01Hz– P00.03 (Max. output frequency) | 50.00 Hz | ◎ | ||
P02.03 | Rated speed of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 1– 36000rpm | Depend on model | ◎ | ||
P02.04 | Rated voltage of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0– 1200V | Depend on model | ◎ | ||
P02.05 | Rated current of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.8– 6000.0A | Depend on model | ◎ | ||
P02.06 | Stator resistor of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.001– 5.535Ω | After motor parameter autotuning finishes, the setting value of P02.06– P02.10 will be updated automatically. These parameters are the basic parameters for high-performance vector control, which will impact the control performance directly. Note: Users cannot change this group of parameters at will. | Depend on model | ○ | |
P02.07 | Rotor resistor of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.001– 65.535Ω | Depend on model | ○ | ||
P02.08 | Leakage induct- ance of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.1– 6553.5 mH | Depend on model | ○ | ||
P02.09 | Mutual induct- ance of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.1–6553.5 mH | Depend on model | ○ | ||
P02.10 | Non- load current of asynch- ronous motor 1 | 0.1– 6553.5A | Depend on model | ○ | ||
P02.11 | Magn- etic satura- tion coeffi- cient 1 for the iron core of AM1 | 0.0– 100.0% | 80.0% | ◎ | ||
P02.12 | Magn -etic satura- tion coeffi- cient 2 for the iron core of AM1 | 0.0– 100.0% | 68.0% | ◎ | ||
P02.13 | Magn- etic satura- tion coeffi- cient 3 for the iron core of AM1 | 0.0– 100.0% | 57.0% | ◎ | ||
P02.14 | Magn- etic satura- tion coeffi- cient 4 for the iron core of AM1 | 0.0– 100.0% | 40.0% | ◎ | ||
P02.15 | Rated power of synch- ronous motor 1 | 0.1– 3000.0kW | Set the parameters of the controlled synchronous motor (SM). To ensure the control performance, se the values of P02.15 to P02.19 properly according to the parameters on the name plate of the SM. Goodrive300 VFDs provide the parameter autotuning function. Correct parameter autotuning depends on the correct setting of the name plate parameters of the motor. To ensure the control performance, configure the standard matched motor for the VFD. If the power of the motor configured is greatly different from that of the standard matched one, the control performance of the VFD degrades significantly. Note: P02.16 to P02.19 may be initialized by resetting the rated power of the motor (P02.15). | Depend on model | ◎ | |
P02.16 | Rated frequ- ency of synch- ronous motor 1 | 0.01Hz– P00.03 (Max. frequency) | 50.00 Hz | ◎ | ||
P02.17 | Number of poles pairs for synch- ronous motor 1 | 1–50 | 2 | ◎ | ||
P02.18 | Rated voltage of synch- ronous motor 1 | 0– 1200V | Depend on model | ◎ | ||
P02.19 | Rated current of synch- ronous motor 1 | 0.8– 6000.0A | Depend on model | ◎ | ||
P02.20 | Stator resistor of synch- ronous motor 1 | 0.001– 65.535Ω | After the motor parameter autotuning is properly complete, the values of P02.20 to P02.22 are updated automatically. These parameters are the benchmark parameters of high-performance vector control, directly affecting the control performance. When P00.15=1 (rotating autotuning), the set value of P02.23 may be automatically updated by autotuning, In this case, there is no need to change the value of P02.23. When P00.15=2 (static autotuning), the set value of P02.23 cannot be updated by autotuning. In this case, calculate and manually change the value of P02.23. | Depend on model | ○ | |
P02.21 | Direct axis induct- ance of synch- ronous motor 1 | 0.01– 655.35mH | Depend on model | ○ | ||
P02.22 | Quad- rature axis induct -ance of synch- ronous motor 1 | 0.01– 655.35mH | Depend on model | ○ | ||
P02.23 | Back EMF constant of synch- ronous motor 1 | When P00.15=2, the set value of P02.23 cannot be updated by autotuning, please count according to the following method. The counter-electromotive force constant can be counted according to the parameters on the name plate of the motor. There are three ways to count: 1. If the name plate designate the counter-electromotive force constant Ke, then: E=(Ke×nN×2π)/ 60 2. If the name plate designate the counter-electromotive force constant E’(V/1000r/min), then: E=E’×nN/1000 3. If the name plate does not designate the above parameters, then: E=P/√3×I In the above formulas: nN is the rated rotation speed, P is the rated power and I is the rated current. Setting range: 0–10000 | 300 | ○ | ||
P02.24 | Initial pole position of synch- ronous motor 1 (reserved) | 0x0000– 0xFFFF | 0 | ● | ||
P02.25 | Identifi- cation current of synch- ronous motor 1 (reserved) | 0%–50% (rated current of the motor) | 10% | ● | ||
P02.26 | Motor 1 over- load prote- ction | 0: No protection 1: Common motor (with low speed compensation). Because the heat-releasing effect of the common motors will be weakened, the corresponding electric heat protection will be adjusted properly. The low speed compensation characteristic mentioned here means reducing the threshold of the overload protection of the motor whose running frequency is below 30Hz. 2: Variable frequency motor (without low speed compensation) Because the heat-releasing effect of the specific motors won’t be impacted by the rotation speed, it is not necessary to adjust the protection value during low-speed running. | 2 | ◎ | ||
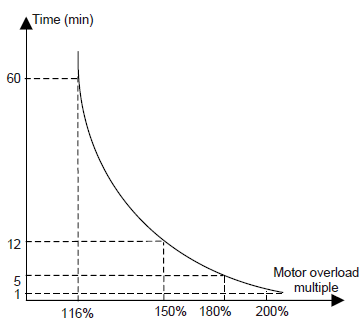
P02.27 | Motor 1 over- load prote- ction coeffi- cient | Times of motor overload M = Iout/(In×K) In is the rated current of the motor, Iout is the output current of the VFD and K is the motor protection coefficient. The smaller K is, the greater M is, and the more likely protection is implemented. When M=116%, protection is performed after motor overload lasts for 1 hour; when M=150%, protection is performed after motor overload lasts for 12 minutes; when M=180%, protection is performed after motor overload lasts for 5 minutes; when M=200%, protection is performed after motor overload lasts for 60 seconds; and when M≥ 400%, protection is performed immediately.
Setting range: 20.0%–120.0% | 100.0% | ○ | ||
P02.28 | Corre- ction coeffi cient of motor 1 power | Correct the power displaying of motor 1. Only impact the displaying value other than the control performance of the VFD. Setting range: 0.00–3.00 | 1.00 | ● | ||
P02.29 | Para- meter display of motor 1 | 0: Display according to the motor type 1: Display all | 0 | ● | ||