Goodrive35 series VFDs are wall, floor and flange mountable devices for controlling asynchronous AC induction motors and permanent magnet synchronous motors. It supports wall, fange, and floor installation.
The diagram below shows the simplified main circuit diagram of the VFD. The rectifier converts three-phase AC voltage to DC voltage. The capacitor bank of the intermediate circuit stabilizes the DC voltage. The inverter transforms the DC voltage back to AC voltage for the AC motor. The brake pipe connects the external brake resistor to the intermediate DC circuit to consume the feedback energy when the voltage in the circuit exceeds its maximum limit.
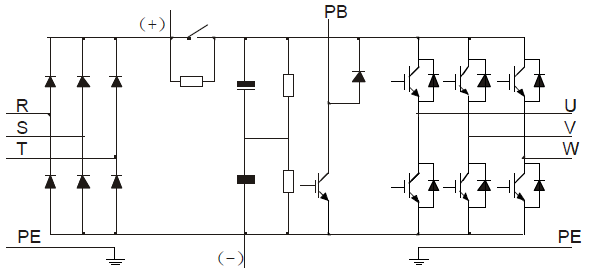
Figure 3‑1 The simplified main circuit diagram (VFDs of 380 V≤30 kW)
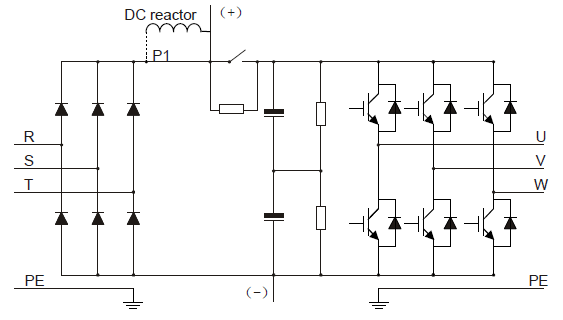
Figure 3‑2 The simplified main circuit diagram (VFDs of 380 V≥37 kW)
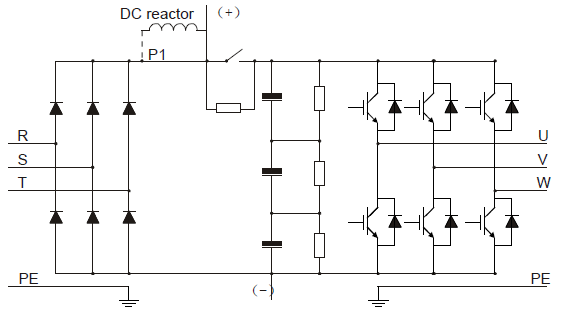
Figure 3‑3 The simplified main circuit diagram (VFDs of 660 V)
Note:
1. The VFDs of 380 V (≥37 kW) supports external DC reactors and external brake units, but it is necessary to remove the copper tag between P1 and (+) before connecting. DC reactors and brake units are optional.
2. The VFDs of 380 V (≤30 kW) supports external brake resistors which are optional.
3. The VFDs of 660 V supports external DC reactors and external brake units, but it is necessary to remove the copper tag between P1 and (+) before connecting. DC reactors and brake units are optional.