| Physical accident may occur if the motor starts up suddenly during autotune. Please check the safety of surrounding environment of the motor and the load before autotune. The power is still applied even the motor stops running during static autotune. Please do not touch the motor until the autotune is completed, otherwise there would be electric shock. |
| Do not carry out the rotation autotune if the motor is coupled with the load, please do not operate on the rotation autotune. Otherwise misacts or damage may occur to the VFD or the mechanical devices. When carry out autotune on the motor which is coupled with load, the motor parameter won’t be counted correctly and misacts may occur. It is proper to de-couple the motor from the load during autotune when necessary. |
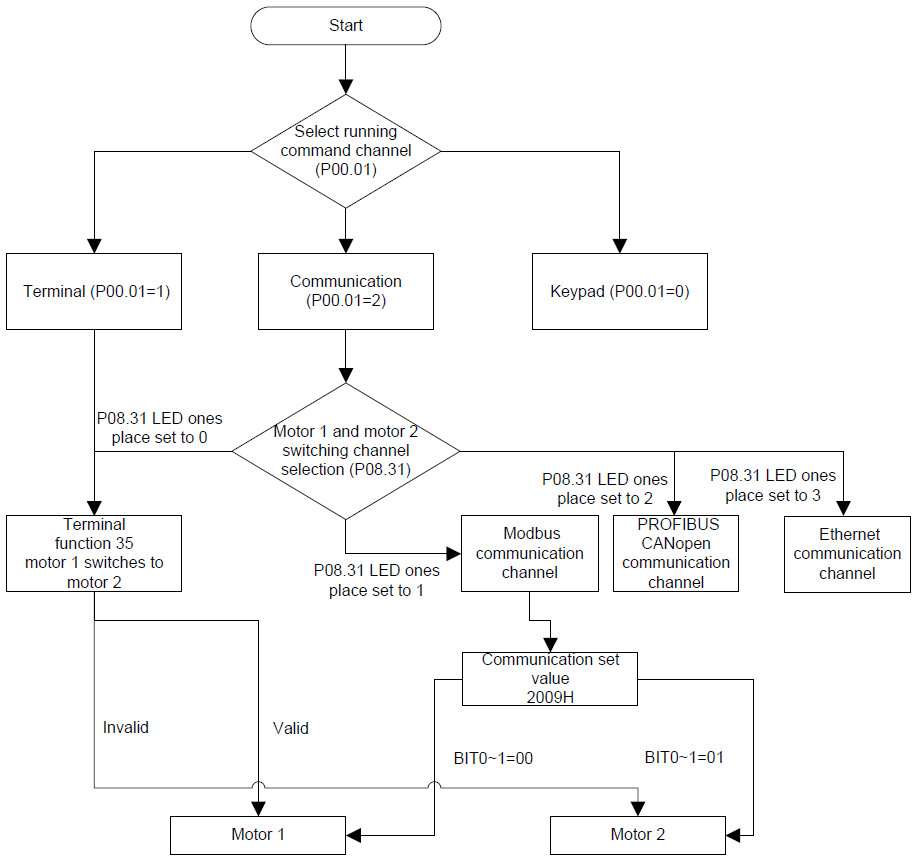
Goodrive35 series VFDs can drive both asynchronous motors and synchronous motors. And at the same time, they can support two sets of motor parameters which can shift between two motors through multi-function digital input terminal or communication.
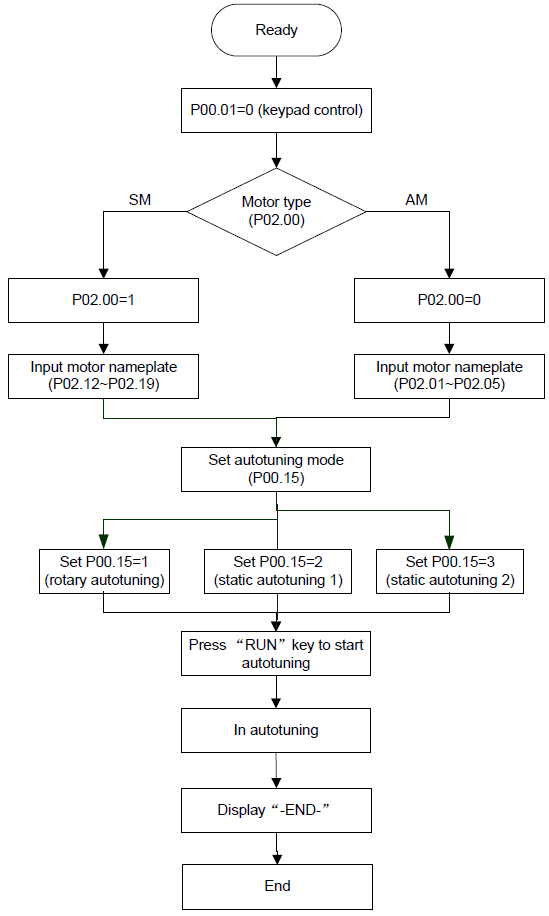
The control performance of the VFD is based on the established accurate motor model. The user has to carry out the motor autotuning before initial running (take motor 1 as an example).
Note:
1. Set the motor parameters according to the name plate of the motor.
2. During the motor autotune, de-couple the motor form the load if rotation autotune is selected to make the motor is in a static and empty state, otherwise the result of autotune is incorrect. The asynchronous motors can autotune the parameters of P02.06–P02.10, while the synchronous motors can autotune the parameters of P02.20–P02.23.
3. During the motor autotune, do not to de-couple the motor form the load if static autotune is selected. Because only some parameters of the motor are involved, the control performance is not as better as the rotation autotune. The asynchronous motors can autotune the parameters of P02.06–P02.10, while the synchronous motors can autotune the parameters of P02.20–P02.22. P02.23 (synchronous motor 1 counter-electromotive force constant) can be counted to attain.
4. Motor autotune only involves the current motor. Switch the motor through P08.31 to carry out the autotune on the other motor.
Relative parameters list:
Function code | Name | Detailed instruction of parameters | Default value |
P00.01 | Run command channel | 0: Keypad running command (LED off) 1: Terminal running command channel (LED flickering) 2: Communication running command channel (LED on) | 0 |
P00.15 | Motor parameter autotuning | 0: No operation 1: Rotation autotuning 2: Static autotuning 1 (autotune totally) 3: Static autotuning 2 (autotune part parameters) | 0 |
P02.00 | Motor 1 | 0: Asynchronous motor 1: Synchronous motor | 1 |
P02.01 | Rated power of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.1–3000.0 kW | Depend on model |
P02.02 | Rated frequency of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.01 Hz–P00.03 (max. output frequency) | 50.00 Hz |
P02.03 | Rated speed of asynchronous motor 1 | 1–36000rpm | Depend on model |
P02.04 | Rated voltage of asynchronous motor 1 | 0–1200 V | Depend on model |
P02.05 | Rated current of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.8–6000.0A | Depend on model |
P02.06 | Stator resistor of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.001–65.535Ω | Depend on model |
P02.07 | Rotor resistor of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.001–65.535Ω | Depend on model |
P02.08 | Leakage inductance of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.1–6553.5 mH | Depend on model |
P02.09 | Mutual inductance of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.1–6553.5 mH | Depend on model |
P02.10 | Non-load current of asynchronous motor 1 | 0.1–6553.5 A | Depend on model |
P02.15 | Rated power of synchronous motor 1 | 0.1–3000.0 kW | Depend on model |
P02.16 | Rated frequency of synchronous motor 1 | 0.01 Hz–P00.03 (max. output frequency) | 50.00 Hz |
P02.17 | Number of poles pairs for synchronous motor 1 | 1–128 | 2 |
P02.18 | Rated voltage of synchronous motor 1 | 0–1200 V | Depend on model |
P02.19 | Rated current of synchronous motor 1 | 0.8–6000.0 A | Depend on model |
P02.20 | Stator resistor of synchronous motor 1 | 0.001–65.535 Ω | Depend on model |
P02.21 | Direct axis inductance of synchronous motor 1 | 0.01–655.35 mH | Depend on model |
P02.22 | Quadrature axis inductance of synchronous motor 1 | 0.01–655.35 mH | Depend on model |
P02.23 | Back EMF constant of synchronous motor 1 | 0–10000 | 300 |
P05.01–P05.09 | Multi-function digital input terminals (S1–S8, HDI) function selection | 35: Shift from motor 1 to motor 2 | |
P08.31 | Motor shifting | 0: Terminal shifting; 1: Modbus communication shifting 2: PROFIBUS/CANopen communication shifting | 0 |
P12.00 | Motor 2 | 0: Asynchronous motor 1: Synchronous motor | 1 |
P12.01 | Rated power of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.1–3000.0 kW | Depend on model |
P12.02 | Rated frequency of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.01 Hz–P00.03 (max. output frequency) | 50.00 Hz |
P12.03 | Rated speed of asynchronous motor 2 | 1–36000 rpm | Depend on model |
P12.04 | Rated voltage of asynchronous motor 2 | 0–1200 V | Depend on model |
P12.05 | Rated current of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.8–6000.0 A | Depend on model |
P12.06 | Stator resistor of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.001–65.535 Ω | Depend on model |
P12.07 | Rotor resistor of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.001–65.535 Ω | Depend on model |
P12.08 | Leakage inductance of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.1–6553.5 mH | Depend on model |
P12.09 | Mutual inductance of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.1–6553.5 mH | Depend on model |
P12.10 | Non-load current of asynchronous motor 2 | 0.1–6553.5 A | Depend on model |
P12.15 | Rated power of synchronous motor 2 | 0.1–3000.0 kW | Depend on model |
P12.16 | Rated frequency of synchronous motor 2 | 0.01 Hz–P00.03 (max. output frequency) | 50.00 Hz |
P12.17 | Number of poles pairs for synchronous motor 2 | 1–128 | 2 |
P12.18 | Rated voltage of synchronous motor 2 | 0–1200 V | Depend on model |
P12.19 | Rated current of synchronous motor 2 | 0.8–6000.0 A | Depend on model |
P12.20 | Stator resistor of synchronous motor 2 | 0.001–65.535 Ω | Depend on model |
P12.21 | Direct axis inductance of synchronous motor 2 | 0.01–655.35 mH | Depend on model |
P12.22 | Quadrature axis inductance of synchronous motor 2 | 0.01–655.35 mH | Depend on model |
P12.23 | Back EMF constant of synchronous motor 2 | 0–10000 | 300 |

